Solar Photovoltaics (PV)
Solar Photovoltaics, or Solar PV for short, is a technology in which daylight is converted into electrical power.
Solar PV takes advantage of energy from the sun to create electricity, that will operate electrical appliances and lighting.
The benefits of solar electricity
- Cut your electricity bills:
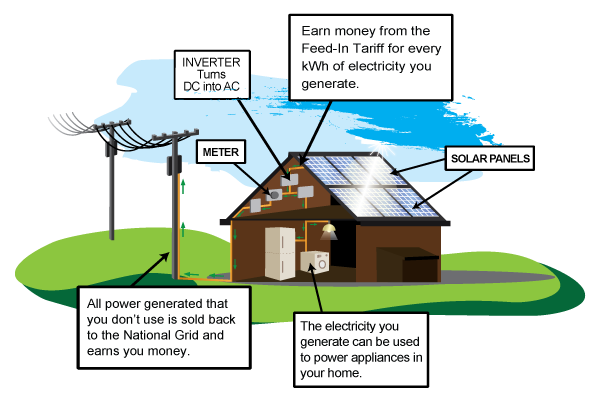
sunlight is free, so once you've paid for the initial installation your electricity costs will be reduced. - Get paid for the electricity you generate:
the government's Feed-In Tariffs pay you for the electricity you generate, even if you use it. - Sell electricity back to the grid:
if your system is producing more electricity than you need, or when you can't use it, you can sell the surplus back to the grid. - Cut your carbon footprint:
solar electricity is green, renewables energy and doesn't release any harmful carbon dioxide] or other pollutants.
A typical home solar PV system could save over a tonne of carbon dioxide per year, that's more than 30 tonnes over its lifetime.
The average domestic solar PV system is 4kWp and on average costs between £5,400 and £7,400 (including VAT at 5%).
Costs have fallen significantly over the last year.
‘On grid’ versus ‘Off-grid’
On Grid systems
Grid-connected photovoltaic systems are the most common type as they make use of the existing mains electricity grid.
They are simpler in design and easier to fit than off grid systems.
The electricity produced during the daytime is either used by the property owner, or directed back into the electricity grid and purchased by a utility company, an arrangement called ‘net metering’.
At night, or on dark days when the panels do not produce sufficient power, electricity will be supplied via normal utility company grid system.
Off Grid systems
Far less common is an ‘off grid’ or ‘stand alone’ system, which produces and stores power independently from the utility grid.
These systems are particularly suitable in remote locations especially those where the property is more than one-quarter mile from the nearest power lines.
The electricity generated by the panels is stored in a bank of rechargeable batteries as DC but in order to power household appliances an inverter will be required to convert the stored DC to AC.